
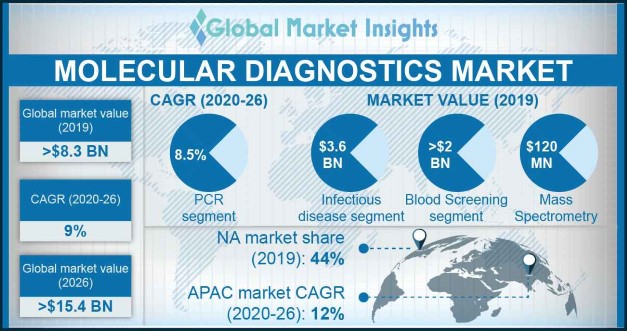
Advances in life sciences and in test technologies are making diagnostics ever more central in the delivery of effective health care. These technologies increasingly are a key component in ensuring that the right treatment gets to the right patient at the right time. Medical diagnostic tests and technologies are at the forefront of health care and personalized medicine. There are many ways that diagnostic technologies can impact the quality and cost of care. In this evolving environment, it is a business imperative for diagnostic manufacturers to understand, demonstrate, and clearly articulate how their offerings can lead not only to better patient outcomes but also create value for a variety of key stakeholders. Points of Entry in the Diagnostics Supply Chain The investment in unifying technology, consolidation and automation of labs, and shift to data-driven healthcare will mark as a trend in this industry. However, high prices of molecular diagnostics tests and unfavourable reimbursement policies will act as the major challenges in the growth of this market. The rapid advancements witnessed in the molecular biology technologies, development of molecular diagnostic technologies to automated processes, growing awareness about molecular diagnostics usage for the detection of different diseases in developing countries is boosting the overall market growth. The market of Molecular Diagnostics market is anticipated to grow enormously owing to factors such as rising geriatric population, increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, increasing adoption of Point-of-care diagnosis, advances in genomics and proteomics, and introduction of technologically advanced products. The growing incidence of infectious diseases and cancer is increasing the demand for molecular diagnostics techniques. Global Molecular Diagnostics Market was valued at US$ 6,242.6 million in 2018 and is anticipated to reach US$ 9,546.2 million by 2025 displaying a reasonable CAGR of 6.3% over the forecast period (2019-2025). Molecular Diagnostics is the detection of genomic variants, aiming to facilitate detection, diagnosis, subclassification, prognosis, and monitoring response to therapy.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
